After all, this is the location where all the other parts will be installed. Motherboards can even limit which types of processors, RAM, HDDs, and SSDs you can buy. Therefore, choosing a good motherboard when building a computer is essential. However, different models are available on the market. And to make matters worse, there are several formats for motherboards. You probably already know the acronyms ATX, Micro ATX, Mini ITX, etc. In this article, you’ll learn about the different types of motherboards. So without further ado, let’s begin!
What is a Motherboard?
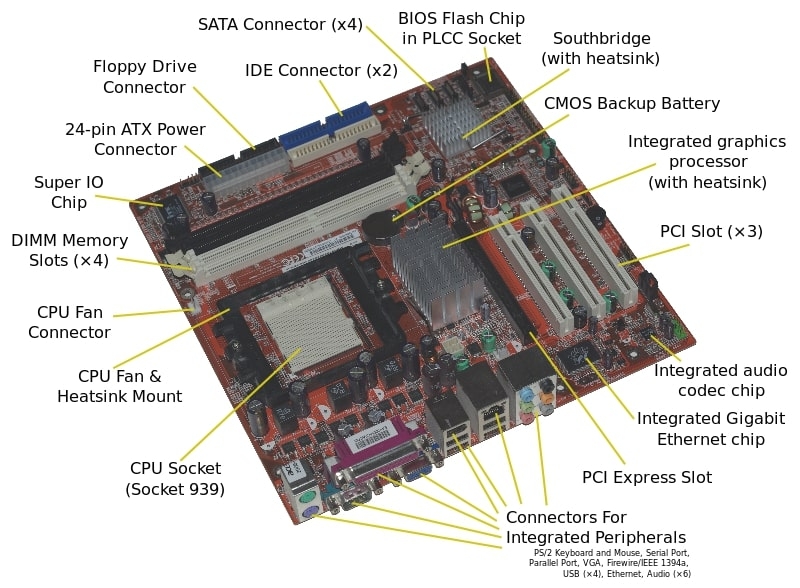
The first thing we need to clarify is what a motherboard is. This is the piece that interconnects all the other components of the computer. The motherboard is connected to specific parts through slots and connectors. For example, the socket is where we install the processor. A slot is provided for fitting RAM modules. PCIe slots are used to connect video cards. SATA and NVMe ports are used for installing HDDs and SSDs. The motherboard also has power connectors, which is where the power supply is plugged in. These are just some of the connectors and slots on a traditional motherboard. All technology is standardized on the market. The components must comply with specific standards developed and approved by the industry. For motherboards, it’s called the form factor. Specifically, it concerns the motherboard’s dimensions. ATX and Micro ATX are the most commonly used standards for desktop computers. PCs with smaller form factors, such as Mini ITX, Nano ITX, and others, are also available.
What are the Components of a Motherboard?
There are many components on a computer’s motherboard, each of which plays a specific role. Here is a description of several motherboard components and their definitions and functions.
Expansion Slots
ISA slots:- Motherboards with these expansion slots were the oldest in history. Identified by their black color, they are found on AT boards. Usually, these slots were used to install a display or sound card. This 16-bit bus is known as Industry Standard Architecture (ISA). PCI Slots. Peripheral Component Interconnect is the full name of PCI. It is one of the most important components of a motherboard today and is widely used to install expansion cards. A 64-bit high-speed bus is supported by PCI. PCI Express:- This is also known as PCIe, a fast and latest component used to provide support for add-on cards on motherboards. There is a full duplex serial bus supported by it. AGP slot:- It is specifically designed for installing the latest graphics cards with an accelerated graphics port (AGP). The AGP interface runs on a 32-bit bus, and high-end gaming display cards can be installed through PCIe and AGP.
RAM Slots
SIMM slots:- In its full form, the module is known as a single inline memory module. Up until 486-based motherboards, these slots were found on older motherboards. The SIMM supports a 32-bit bus. DIMM slots:- Double inline memory modules are the full form of DIMM. This RAM slot runs on a faster 64-bit bus, the latest version. DIMMs used on laptop boards are called SO-DIMMs.
CPU Socket
CPU sockets are used to install the processor on motherboards. The following are some of the most important sockets. Socket7:- It is a 321-pin socket supported by an older generation of processors such as Intel Pentium 1/2/MMX, AMD K5/K6, and Cyrix M2. Socket370:- Celeron processors and Pentium-3 processors are supported by the 370-pin socket. Socket 775:- It supports Inter dual-core, C2D, P-4, and Xeon processors with a 775-pin connector. Socket 1156:- It is an 1156-pin socket found on the latest motherboards that support Intel i3, i5, and i7 processors. Socket 1366:- This socket supports the latest Intel i-7 900 processor with 1366 pins.
Power Connector
There are connectors mounted on the motherboard where power is received from SMPS. AT connector:- There are two 6-pin male connectors on old motherboards. ATX connector:- Female connectors with 20 or 24 pins are the latest in the series of power connectors. It is found in all the latest types of motherboards.
IDE Connector
Disk drives are interfaced through the Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) connectors. An IDE hard disc drive is connected with a 40-pin male connector, and a floppy disk drive is connected with a 34-pin male connector.
SATA Connector
Serial Advance Technology Attachment(SATA) connectors are 7-pin connectors that interface with the latest SATA hard drives and optical drives. In comparison to IDE interfaces, they are much faster.
BIOS
This system is known as the Basic Input Output System or BIOS. An integrated chip on a motherboard is part of the motherboard. Your computer’s BIOS setting can be modified by entering this chip, which contains all the motherboard’s information and locations.
CMOS Battery Header
The battery or cell is a lithium-type battery with a voltage of 3.0 volts. This cell stores the BIOS information, and its full name is a Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor.
Co-Processor
The coprocessor is an important motherboard component that assists the central processor with mathematical calculations and computer graphics.
Cabinet Connections
It has many buttons connected to the motherboard from the cabinet where it is installed. The most common connectors are the Power Switch, Reset Switch, Front USB, Front Audio, and Power Indicator (LED). I/O interface connectors:- When it comes to determining the overall speed of your computer, selecting the right motherboard is crucial. Understanding the various components on a motherboard will make it easier for you to assemble your PC or resolve basic hardware problems.
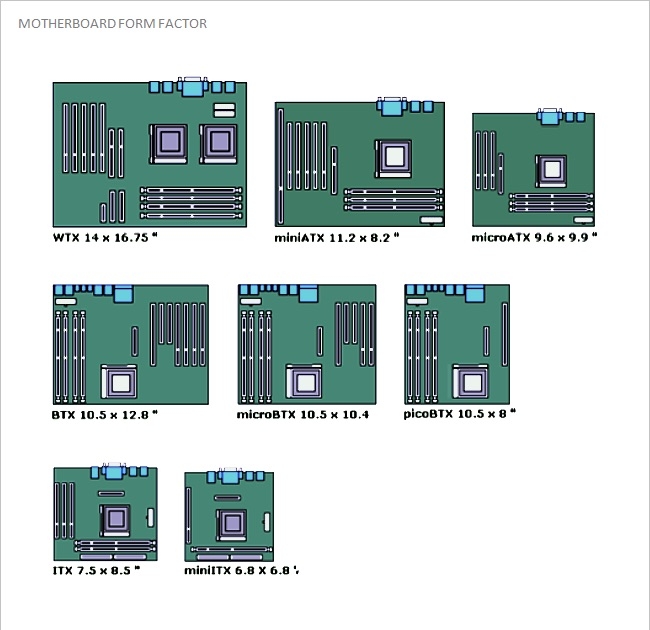
Different Types Of Motherboards
You can find various types of motherboards in the market, and each one is designed to support a specific need. Here are some common motherboard types.
AT Motherboard
The motherboards of these computers are larger by hundreds of millimeters, so they are not suitable for mini desktop computers. It is also difficult to install new drivers due to the larger physical size. These motherboards use sockets and six-pin plugs for power connections. The power connectors are not easily identifiable, so users have difficulty connecting and using them. Motherboards of this type were popular in the 1980s and lasted for a long time.
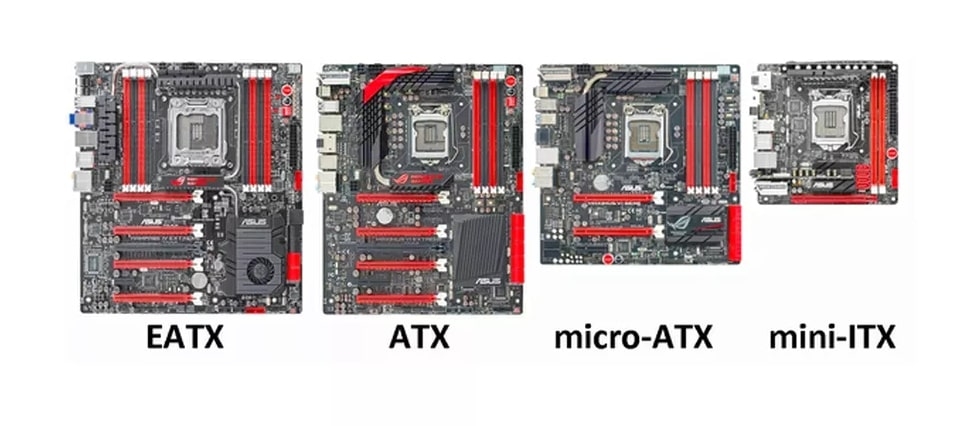
ATX Motherboard
The full form of ATX is Advanced Technology Extended, the most popular type of motherboard. As an improvement over AT motherboards used previously, Intel released the ATX motherboards in the mid-1990s. A significant difference between these boards and AT counterparts is that they allow components to be interchanged. Additionally, because the dimensions of this motherboard are smaller than those of an AT motherboard, there is sufficient space for the drive bays. Also, the connector system of the board had been improved. At motherboards, various add-ons could be fitted into additional slots on the back plate. This motherboard is still in existence today, is one of the most popular motherboards ever, and has been the basis for many other factors.
Micro ATX Motherboard
A Micro ATX board is a scaled-down version of an ATX board. There is only one difference between ATX and Micro ATX: their sizes. All other specifications, such as the positions of holes and components, remain the same. Rather than 12-by-9.6 inches, it is 9.6-by-9.6 inches. This board was designed to fit in small computer cases. Since it is smaller than an ATX board, it has fewer expansion and memory slots. Although they are smaller, they do not provide less computing power as a result. There are even some gaming computers that use these boards.
LPX Motherboard
There were two improvements to this board over earlier versions. Firstly, the Input and Output ports were relocated to the back, and secondly, a Riser card was introduced to facilitate more slots and better connection. Several of these features were included in the AT motherboard. Its main downside is the lack of Accelerated Graphic Port (AGP) slots, which means it connects directly to PCI. These motherboards had issues that were addressed in NLX boards.
BTX Motherboard
As the name implies, BTX stands for Balanced Technology Extended. It’s designed to handle new technology’s power requirements, resulting in increased heat generation. As a result of concentrating on low-power CPUs, Intel stopped the development of BTX boards in the mid-2000s.
Pico BTX motherboard
Pico BTX motherboards allow for even smaller BTX standard cards to be manufactured. Since this motherboard is smaller than many current “micro” motherboards, it has been called “Pico.” There are two sizes of BTX motherboards, but they share a common top half. There is support for only one or two expansion slots. Despite its unique features, it supports the demands of digital applications with its half-height or riser cards.
Mini ITX Motherboard
The Mini-ITX form factor is 6.7 by 6.7 inches and is suitable for low-power motherboards. In 2001, VIA Technologies designed it. Most of these are used in small form factor (SFF) computers. The low power consumption of Mini-ITX boards also makes it easy for them to be cooled. Their architecture suits them for home theater PCs and systems where excessive fan noise can compromise the cinematic experience. A Mini-ITX board has the same four mounting holes as an ATX motherboard, and its back plate and expansion slots are located in the same places. However, earlier versions of the ATX had one of the holes optional. As a result, Mini-ITX boards can be used in places designed for ATX, micro-ATX, and similar ATX boards. Occasionally, riser cards are used and can even be used with two-slot riser cards, even when they cannot be used with all boards. These boards cannot be used with PCI riser cards supplied with cases.
Nano ITX Motherboard
The Nano ITX motherboard is even smaller than the Mini ITX motherboard. It has a dimension of 4.7 by 4.7 inches. Power consumption is very low due to the fully-integrated design of these boards. Most commonly, it is used in smart entertainment devices like smart TVs, in-vehicle devices, media centers, and personal video recorders.
Pico ITX Motherboard
Finally, we have Pico ITX, the smallest motherboard. The dimensions of a Pico ITX motherboard are only 3.9 by 2.8 inches. It is approximately 75% smaller than the Mini ITX. ty This board was designed for the IoT market, where devices get smaller as time passes. It has low power consumption and is based on the x86 architecture. This is an excellent choice for embedded systems like in-vehicle computers, industrial automation, and digital signatures.
Conclusion
I hope you enjoyed this article on types of motherboards. As you can see, there is a type of motherboard for every need. If you have any further queries or thoughts regarding this article, feel free to let us know in the comment section below. Thanks for reading!
First Look at the Asus Prime Z790-A WiFi Raptor Lake Motherboard Motherboard Buying Guide: All You Need to Know MSI Announces World’s First Inbuilt Liquid Cooled Motherboard